Edward de Bono, the pioneer of Lateral Thinking, introduced the Plus/Minus/Interesting (PMI) strategy to evaluate ideas and issues from multiple perspectives. It’s a straightforward yet powerful tool for critical thinking, structured analysis, and balanced decision-making.
How PMI works?
To apply PMI, grab a sheet of paper (or a digital board), divide it into three columns, and work through the following steps:
- Plus (Positive Points): List the benefits, strengths, or advantages of the idea, issue, or situation.
- Minus (Negative Points): Record the risks, challenges, or downsides.
- Interesting Points: Capture neutral or thought-provoking aspects—questions, uncertainties, or possibilities that deserve further exploration.
- Conclude: Review all three lists to analyze the full picture and make a more informed decision.
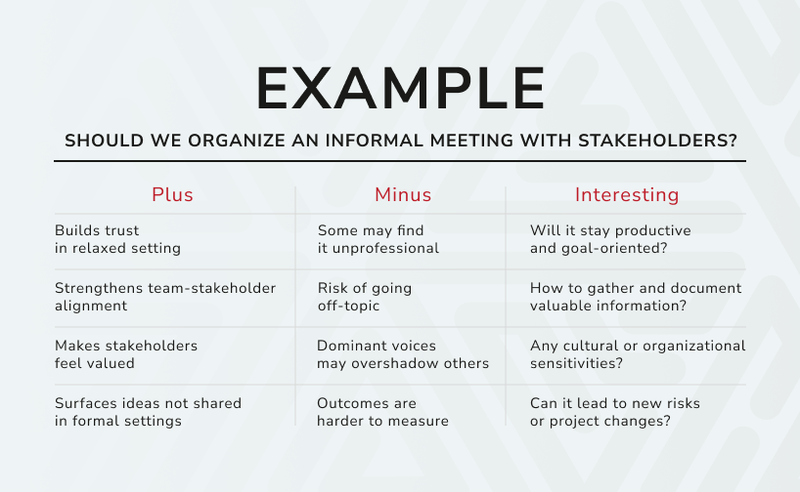
Why use PMI in Project Management?
The PMI technique is especially valuable in project environments where decisions must balance competing priorities and perspectives. It helps to:
✨ Encourages balanced decision-making
✨ Avoids biased perspectives
✨ Promotes team collaboration
✨ Simplifies complex issues
Tip: Apply PMI during brainstorming sessions, project planning, or risk assessment workshops to ensure that every angle is considered before moving forward.
The PMI (Plus, Minus, Interesting) strategy is not about finding the “right” or “wrong” answer. Instead, it’s about creating a 360° view of an idea or issue, so project teams can make decisions with confidence, clarity, and consensus.
Downloads
Supplemental Resources
Plus, Minus, Interesting: PMI in Project Management.pdf
Learn more about this powerful tool for critical thinking, structured analysis, and balanced decision-making.