Effective project planning lays the foundation for successful project execution. A detailed and explicit plan ensures that all project elements fit perfectly together, minimizing rework and delays. Conversely, a poorly defined plan with unspecified project components leads to excessive rework and inevitable delays.
To prevent schedule and budget overruns, project managers must define the project scope at the initial stage. The creation of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a critical step in this process. It serves as a framework of what has to be delivered. Something like a ‘family tree’ with all the components of the project that eventually define the total scope.
What is WBS?
According to the Project Management Institute’s Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), the WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. Each successive level of the WBS represents a more detailed component of the project, which can include products or services.
WBS Types
The visual and hierarchical scheme of the WBS represents the work to be done. The nature of the WBS allows for various approaches to deconstruct the work. Some of the most common methods include deliverable-based, phase-based, and team-based WBS.
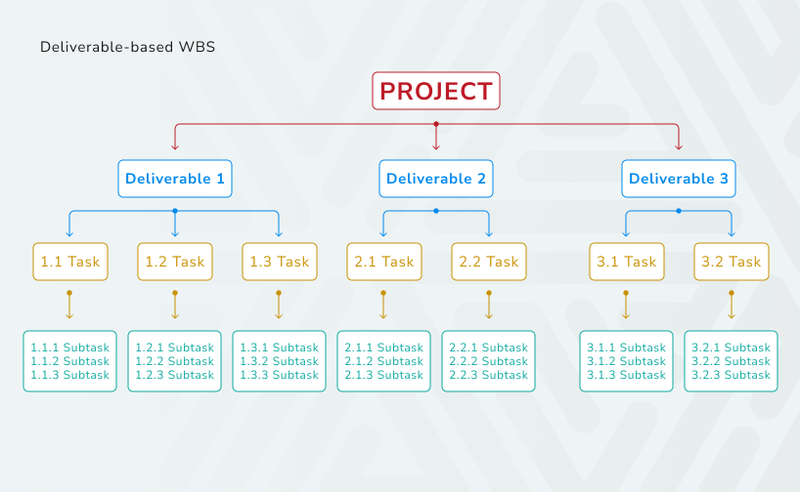
- Deliverable-based WBS. This approach organizes tasks around the project deliverables. Each deliverable serves as a category for related tasks, simplifying the tracking of progress towards specific objectives.
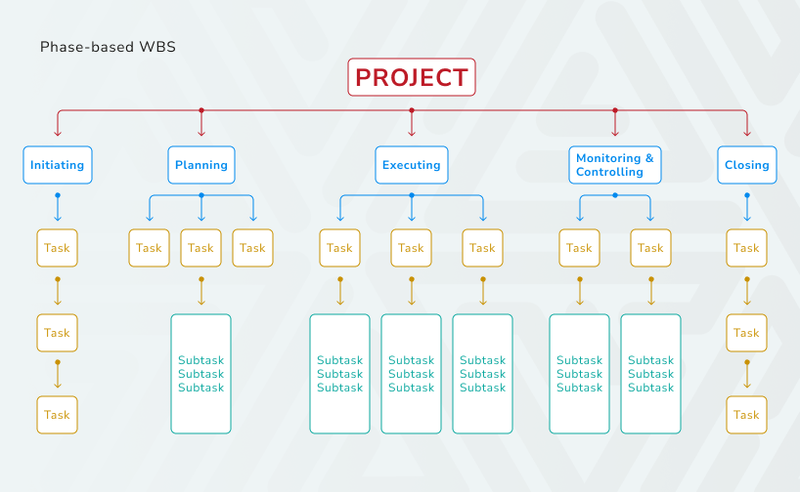
- Phase-based WBS. In this method, tasks are grouped according to the project lifecycle, with deliverables represented as outcomes at the bottom of the hierarchy.
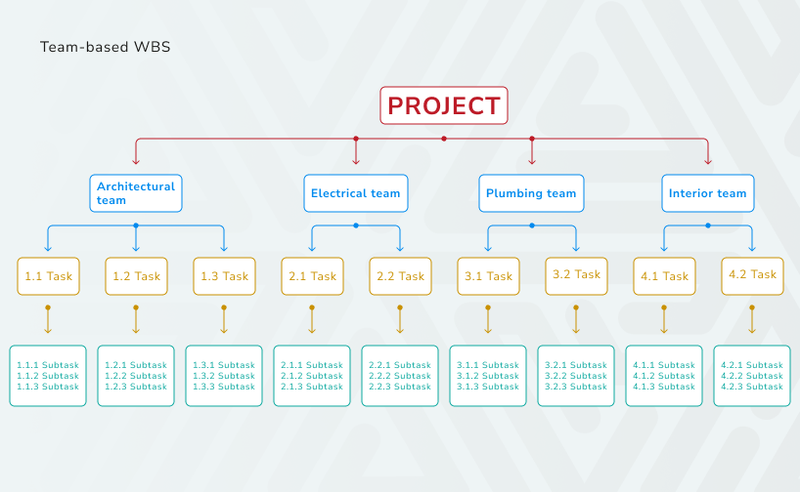
- Team-based WBS. This approach helps to organize tasks according to teams or departments responsible for each element of the project. It simplifies resource allocation within different teams that work on the project and clarified team responsibilities.
Why Use WBS?
WBS is the initial component of a project schedule development. It specifies not only all the work that needs to be done, but also sets a clear plan of tasks in order to reach the project goals and objectives as per the Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM).
Key Benefits of Using a WBS:
- Clarifies Project Scope: The WBS visualizes project components such as scope, stages, tasks, and deliverables. This clarity ensures that all team members are focused on the end goal and understand their responsibilities.
- Simplifies Task Assignment: By dividing the work into specific tasks and packages, the WBS makes it easier to assign responsibilities to team members. This fosters effective planning and execution.
- Improves Communication: The WBS details the work, assigned specialists, and their steps. It also communicates project progress, ensuring that everyone stays informed and aligned.
- Facilitates Risk Management: The WBS is presented before any work begins, providing a comprehensive view of project requirements. This includes time and resource allocation, helping the team identify potential risks and plan phases accordingly.
- Enhances Scheduling: A well-structured WBS serves as a guide for estimating and scheduling the project. It ensures that all tasks are accounted for and helps keep the project on track.
Creating a WBS
To understand the process of creating a WBS better, here is a detailed guide with every step explained:
- Define the Project Scope: Begin by clearly defining the project scope. This includes identifying the deliverables, constraints, and assumptions. A well-defined scope sets the foundation for creating an accurate WBS.
- Identify Major Deliverables: Break down the project into major deliverables. These high-level components form the first level of the WBS.
- Decompose Deliverables into Tasks: Decompose each major deliverable into smaller, manageable tasks. Continue breaking down tasks until you reach a level where each task can be assigned to a team member or group.
- Assign Responsibility: Assign responsibility for each task to the appropriate team members or departments. Ensure that each team member understands their role and responsibilities.
- Validate the WBS: Review the WBS with the project team and stakeholders to ensure completeness and accuracy. Make adjustments as necessary to address any gaps or inconsistencies.
- Maintain the WBS: Update the WBS throughout the project lifecycle to reflect any changes in scope or tasks. This ensures that the WBS remains a relevant and useful tool.
The Work Breakdown Structure is a vital tool for effective project management. It provides a clear and organized framework for defining and managing the project scope, simplifying complex projects into manageable tasks. By improving communication, facilitating risk management, and enhancing scheduling, the WBS helps ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget. Implementing a WBS effectively can significantly enhance project outcomes and contribute to overall project success.
Downloads
Supplemental Resources
Work Breakdown Structure Template.xlsx
Effective project planning lays the foundation for successful project execution. Download a free WBS template to minimize rework and delays.