A project doesn’t seem so manageable when you need to align numerous moving parts of a substantial project, does it? And if this alignment process goes wrong, the project slows down and it leads to productivity decrease eventually.
Integration Management stands as a key knowledge area within project management, synchronizing various processes and systems to facilitate smooth execution and achieve goals and objectives.
Why is it so important?
The critical role of Project Integration Management comes with its adept coordination of diverse project aspects. Project managers are responsible for having the foresight to various components throughout the entire project lifecycle. Tasks such as budget allocation, communication strategies, risk and scope definition, scheduling, quality assurance, and change management necessitate a profound understanding of the intricate inter-dependencies among these parts. Any project scope changes, for instance, can lead to delays in schedule and cost overruns.
The basics
All project managements processes are logically combined and somehow touch the Project Management Process Groups:
- Initiating
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closing
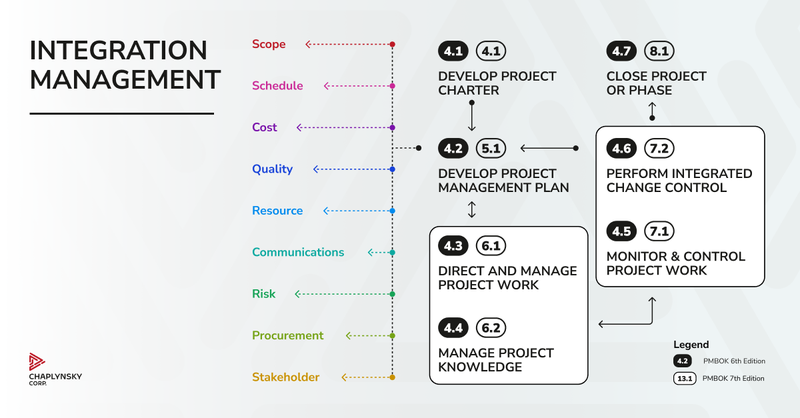
Here are 7 processes included in Project Integration Management:
- Develop Project Charter (Initiating). Referring to Project Initiating group, the aim of the process is to establish the goals of the project and ensure the approval of stakeholders through project objectives.
- Develop Project Management Plan (Planning). This process is included into Planning and brings all the aspects into a single document. The aspects may involve budget, risks, goals, scope, change management.
- Direct and Manage Project Work (Executing). Within the Executing process, the project manager takes charge of directing the team, holding meetings with stakeholders, and tracking the project progress.
- Manage Project Knowledge (Executing). This process is also provided during the Executing period and includes managing the information presented by a project to use for future projects.
- Monitor and Control Project Work (Monitoring and Controlling). The purpose of this step is keeping track of the project, identifying any possible deviations, and correcting them.
- Perform Integrated Change Control (Monitoring and Controlling). This process involves reviewing the changes requested, ensuring they don’t exceed the scope, which can result in requirements increase.
- Close Project or Phase (Closing). As all the work on the project is completed, it is time to finalize the project, hold a final stakeholder meeting, and close the contract.
Things to keep in mind
What is also worth mentioning is that every project management process presents at least one output, coming from a certain input, as a result of specific tools and techniques.
Thus, Project Integration Management serves as the basis of effective project execution. It ensures seamless project development from inception to completion due to processes integration, cohesive communication, and project aspects management.